Lipids are very important in diet, not only for the high energy intake but also for their functionality in cell membranes and because they can be stored.

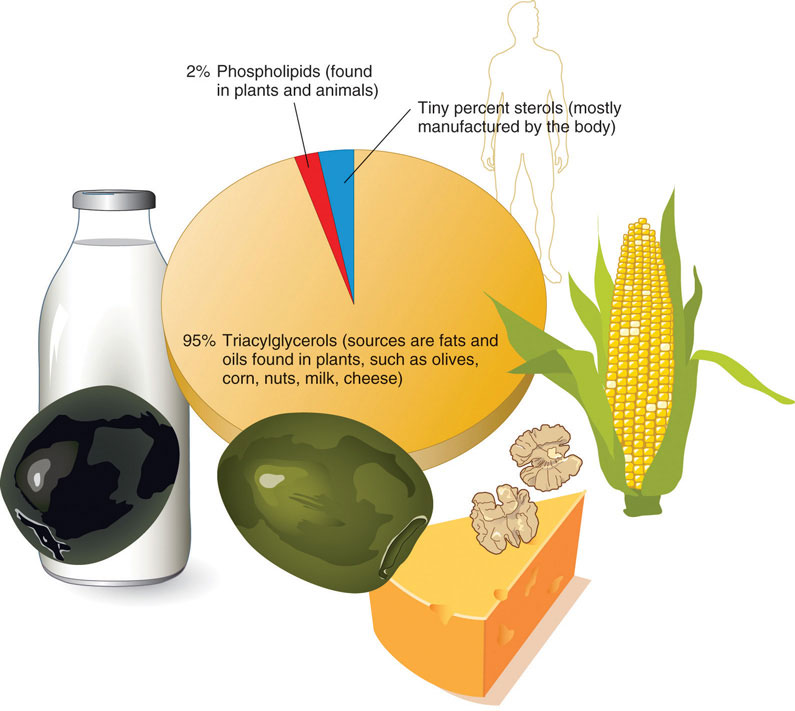

Triglycerides are the most common lipids, they are present in solid food because they don't have the phosphate group as phospholipids. Phospholipids are present in liquid state, for instance oils. The least known lipid is sterol or steroids, for example, a sterol is Cholesterol. Cholesterol helps to synthesize sex hormone, vitamin D and bile salts.

Fats have micronutrients, such as fat-soluble vitamins, they improve intestinal absorption or increase of bioavailability. Fats also increase the bioavailability of phytochemicals, such as lycopene or carotenes, that have anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties, among others.
Hydrolytic rancidity:
Oxidative rancidity:
Bibliography:
https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/an-introduction-to-nutrition/s09-01-what-are-lipids.html
https://app.kognity.com/study/app/chemistry-sl-fe-2016/option-biochemistry/lipids/lipids-health-and-energy/
Hydrolytic rancidity:
- Hydrolysis produces butanoic acid.
- This acid has an unpleasant odor, makes rancid fat.
- Diary products that have high levels of water are exposed to hydrolytic rancidity.
- This is minimized with refrigeration.
- Caused by heat and humidity but catalyzed by Lipase enzyme.
Oxidative rancidity:
- Oxygen reacts with double bonds.
- Catalyzed by light.
- Ketones and aldehydes are produced, and they have unpleasant aroma.
- Food with high content of unsaturated fats is exposed to oxidative rancidity.
Bibliography:
https://2012books.lardbucket.org/books/an-introduction-to-nutrition/s09-01-what-are-lipids.html
https://app.kognity.com/study/app/chemistry-sl-fe-2016/option-biochemistry/lipids/lipids-health-and-energy/
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario