Lipids are macromolecules (polymer) made by fatty acids (monomer).

Carboxilic acid is the ¨head¨ and the fatty acid chain is the ¨tail¨
As they are insoluble in water, they have a head and a tail, as seen in the picture.
- Triglycerides: are 3 chains of fatty acids bonded to one molecule of glycerol. There can be 3 types.
Saturated fats: single bonds, linear structure, solid. Example: Stearic acid.
Monounsaturated fats: have 1 double bond, bent structure. Example: Oleic acid.
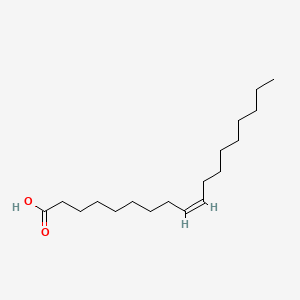
Polyunsaturated fats: more than 1 double bond, bent structure.

Triglycerides formation process is condensation to create a ester linkage, while the reverse process is hydrolysis.

2. Phospholipids: derived from triglycerides, phospholipids are 2 chains of fatty acids bonded to one glycerol molecule and one phosphate group.

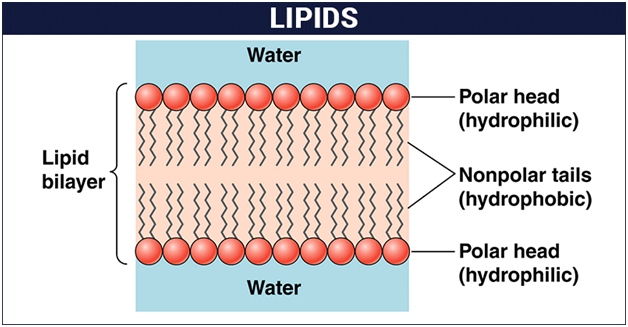
As the phospholipid has a phosphate group, it is soluble in water because of the ion-dipole.
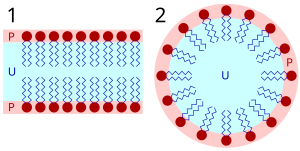
Phospholipids heads are in contact with water (hydrophilic) while their tails get protected (hydrophobic). They arrange in a bilayer, as number 1 in the photo, and micelle, as number 2 in the photo.
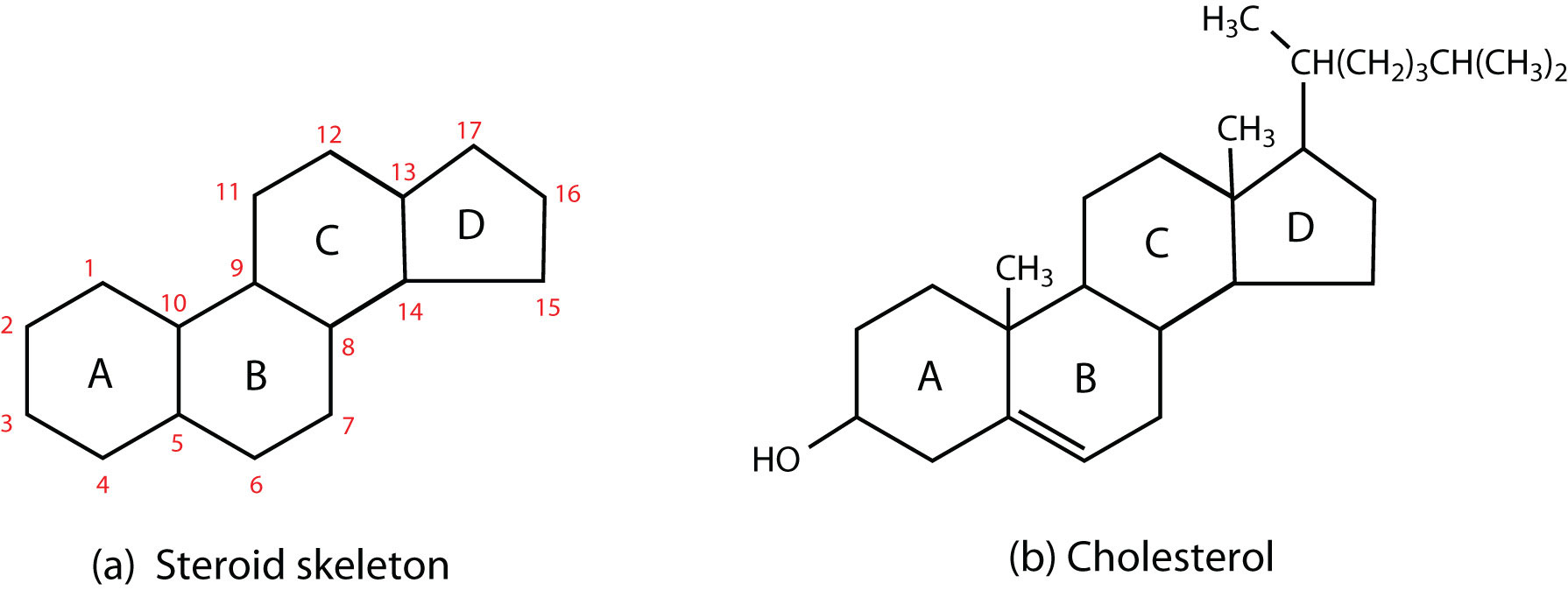
3. Steroids: they arrange themselves to form hormones. Consist in 17 carbon atoms arranged in rings. There are substituted functional groups to form different hormones.
Bibliography:

Comentarios
Publicar un comentario