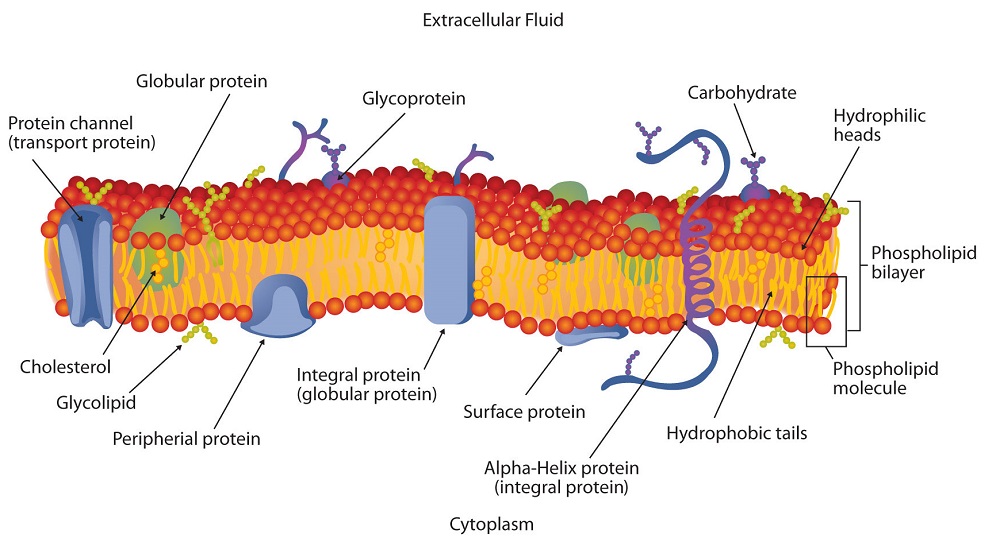
Lipids are constituent of cell membranes because of their bilayer and crystal structures.
Lipids are chemical messengers that send information to other cells and organelles.
Lipids are transported by lipoproteins, which are insoluble in blood. Cholesterol moves through the body inside lipoproteins. There are 2 types of lipoproteins:

Lipids are chemical messengers that send information to other cells and organelles.
- Insolubility in water make them candidates.
- Lipids bond with proteins to carry information.
- Internal components respond to external signals of the lipid bilayer membrane.
- Outside signal is the primary messenger.
- Chemical transmitter do not enter the cell, so lipids are the secondary messenger in the intracellular membrane.
- Lipids are mediators of the membrane responses.

Fat that is kept after lipolysis helps to the maintenance of temperature because of the reserves under the skin.
Lipids are transported by lipoproteins, which are insoluble in blood. Cholesterol moves through the body inside lipoproteins. There are 2 types of lipoproteins:
- Low density lipoprotein: made up by saturated trans fats. Increases cardiovascular disease because it transports cholesterol to arteries, and excess can build up a wall.
- High density lipoprotein: made up by unsaturated fats, stimulates energy storage, insulates and protect organs, essential fats reduce risk of heart disease. Helps to get rid of cholesterol excess.
- Is good to have HDL in a high level but LDL in a low level.
Bibliography:
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario